How to Build a Pole Barn with Strong Metal Beams and Support Posts
A pole barn, also known as a post-frame building, offers a versatile and cost-effective solution for a range of needs, from agricultural storage to workshops and garages. While traditional wood framing is common, utilizing strong metal beams and support posts elevates the structure's durability, longevity, and resistance to the elements. This comprehensive guide outlines the process of constructing a sturdy pole barn using high-quality metal components.
1. Planning and Design:
Determine the Purpose: Define the primary function of the pole barn â€" storage, workshop, living space, etc. This will dictate the size, layout, and specific features required.
Site Selection: Choose a level or slightly sloped site with good drainage to ensure structural integrity and prevent water damage. Consider access for construction equipment and future vehicle movement.
Building Codes: Consult local building codes and regulations for requirements regarding foundation types, structural requirements, and permitted uses.
Design and Engineering: Engage a structural engineer to create detailed plans for the pole barn, including foundation design, beam specifications, post sizing, and roof system.
Materials Selection: Specify the desired metal materials, including structural steel beams, support posts, and roofing materials. Consider factors like corrosion resistance, fire resistance, and aesthetic preferences.
2. Foundation Construction:
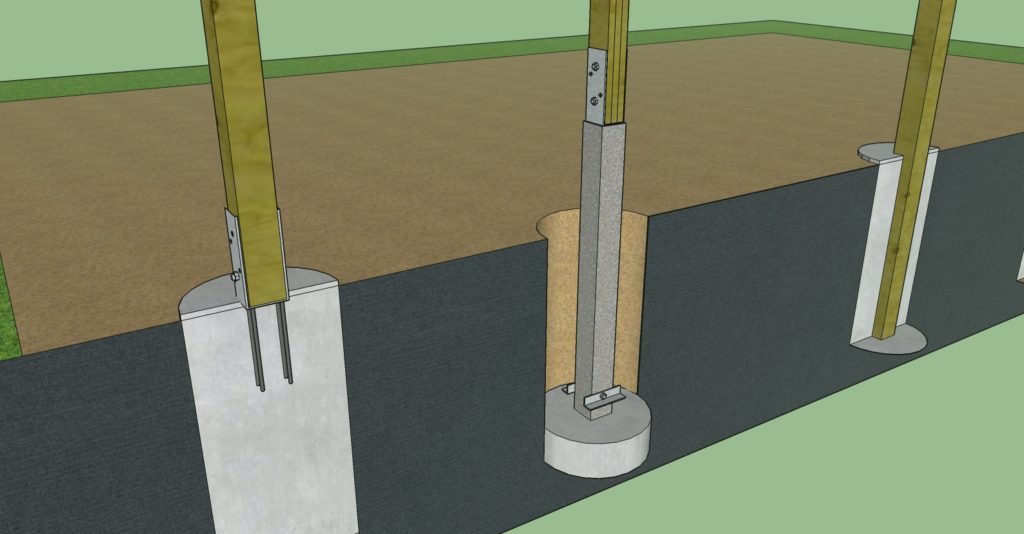
Foundation Type: The most common foundation types for pole barns include concrete piers, helical piers, and concrete slabs. The choice depends on soil conditions, building size, and local codes.
Pier Construction: For concrete piers, excavate holes to the specified depth and width. Install rebar cages for reinforcement and pour concrete, allowing for proper curing time.
Helical Pier Installation: Use specialized equipment to drive helical piers into the ground until they reach the desired depth. This is an excellent option for challenging soil conditions.
Concrete Slab: Pour a reinforced concrete slab for larger buildings or those requiring a level floor. Ensure proper drainage and slope to prevent water accumulation.
3. Erecting the Support Posts:
Post Material: Choose high-strength steel or galvanized steel posts for maximum durability and resistance to corrosion.
Post Size: The engineer's plans will specify the required post size and spacing based on the building's dimensions, snow load, and wind load requirements.
Post Installation: Securely attach the support posts to the prepared foundation using anchor bolts or other approved methods. Ensure plumbness and proper spacing.
4. Installing Metal Beams:
Beam Material: Select structural steel beams, preferably I-beams or wide-flange beams, for optimal strength and load-bearing capacity.
Beam Sizing: The engineer's plans will indicate the required beam sizes and spans based on the intended use of the building and anticipated loads.
Beam Installation: Connect the beams to the support posts using high-strength bolts or welding techniques. Ensure proper alignment and connection to transfer load effectively.
Purlin Installation: Install purlins, typically lightweight steel sections, perpendicular to the beams to provide support for the roof sheathing.
5. Roofing Construction:
Roof Sheathing: Choose a suitable roofing material for the pole barn's purpose and local climate. Options include metal panels, corrugated steel, or plywood covered with asphalt shingles.
Roofing Installation: Install the roofing material according to manufacturer specifications, ensuring proper fastening and sealing to prevent leaks.
Gutters and Downspouts: Install gutters and downspouts to manage rainwater runoff and prevent water damage to the building.
6. Wall Construction:
Wall Sheathing: Choose a wall cladding material that suits the building's purpose, such as metal siding, wood siding, or composite panels.
Insulation: Install insulation to provide thermal protection and improve energy efficiency. Consider various insulation options depending on climate and desired insulation levels.
Finishing Touches: Add windows, doors, and other desired features to complete the building's exterior.
7. Interior Finishing:
Flooring: Install the chosen flooring material, such as concrete, epoxy, or wood, depending on the building's intended use.
Utilities: Install plumbing, electrical wiring, and heating/cooling systems as required.
Interior Walls and Ceilings: Finish interior walls and ceilings with drywall, paneling, or other appropriate materials.
Advantages of Metal Beams and Support Posts:
Durability: Steel is inherently strong and resistant to rot, decay, and insect infestations.
Longevity: Metal structures are designed for long-lasting performance, withstanding harsh weather conditions and resisting the effects of time.
Fire Resistance: Steel is non-combustible, providing a significant safety advantage compared to wood framing.
Low Maintenance: Metal surfaces require minimal upkeep, reducing long-term maintenance costs.
Sustainability: Steel is a recyclable material, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Conclusion:
Constructing a pole barn with robust metal beams and support posts offers numerous advantages over traditional wood framing. By following these steps, you can build a durable, long-lasting, and secure structure suitable for a wide range of purposes. Remember to engage professionals, such as structural engineers and qualified contractors, to ensure the project's success and meet all local building codes and regulations. With careful planning, quality materials, and expert execution, your pole barn will stand strong for years to come.



0 comments:
Post a Comment